The interior of the car is a very complex small environment (Figure 1). There are various factors such as high temperature, cold, friction, vibration, organic solvents, inflammable, and interference noise on the car. The car wires are also different from ordinary wires and cables. According to the laying position and functional requirements, the wires should have various properties such as heat resistance, cold resistance, oil resistance, wear resistance, flame retardancy, and interference resistance. Therefore, the automotive wires should be selected according to the different environments and functions of the wires. For example:
☞ The ambient temperature around the engine in the front compartment is high, and there are many corrosive gases and liquids. Therefore, we must use wires that are resistant to elevated temperatures, corrosion, oil vibration, and friction. The Temperature resistance of the wires in the front compartment of the car is required to be between – 40 ° C and 125 ° C.
☞ The environment of the cab is comfortable, and the temperature resistance of the used automobile wires is between – 40~85 ° C, which can meet the requirements.
☞ In addition, according to distinct functions, the selection of wires for different electrical systems of automobiles is also different.

1. What is Automotive Wire?
Automotive wire is the main part of the automotive wire harness, which is mainly used to carry the current required by the load.
● Copper core wire with an insulating layer is used to transmit signals and power from one end to the other.
● Low voltage wires (small and medium-sized vehicles: 12V, large and heavy vehicles: 24V) are the main wires used for automobiles, and there are more than one thousand kinds of wires used now. As cars become more diversified, the functions of the wires used become diversified. With the development of hybrid electric vehicles and pure electric vehicles, more and more high-voltage harnesses are used in vehicles. However, this article only discusses low-voltage wires.
● The important parameter of the wire is the current carrying capacity, which is affected by the wire diameter (cross-sectional area of the wire), wire length, wire resistivity and ambient temperature.

2. Composition of Automotive Wire
✔ Core wire (also known as conductor: soft metal twisted together): Made of high-conductivity material (copper or aluminum) that connects circuits, allows current to flow and transmits electrical signals.
✔ Insulation: To prevent short circuits (to prevent contact with other circuits), wrap the conductor with PVC and other materials for insulation protection.

3. Standard of Automotive Wire
✔ Chinese standard
● Characteristic: The Chinese standard wire is characterized by thick insulation, soft and good ductility
● Example: GB/T8139,JB/T8139,QC/T730,QC/T1037

✔ Japanese standard
● Characteristic: The Japanese standard wire is characterized by thin insulation and good flexibility
● Example: JASO_ D608, JASO_ D609, JASO_ D611
|
Conductor |
Finished product |
Maximum Resistance at 20ºC |
|||
|
Cross Sectional Area |
No. of Cond |
Insulation Thick. |
Outside Thick. |
Weight |
|
|
mm2 |
No./mm |
mm |
mm |
kg/km |
Ω/mm |
|
0.3 |
7/0.26 |
0.3 |
1.4 |
5.1 |
50.20 |
|
0.5 |
7/0.32 |
0.3 |
1.6 |
7.25 |
32.70 |
|
0.85 |
19.0.24 |
0.3 |
1.8 |
10.3 |
21.70 |
|
0.85 |
7/0.4 |
0.3 |
1.8 |
10.45 |
20.80 |
|
1.25 |
19/0.29 |
0.3 |
2.1 |
14.66 |
14.90 |
|
2 |
19/0.37 |
0.4 |
2.7 |
24.0 |
9.00 |
|
0.3F |
19/0.16 |
0.3 |
1.4 |
5.18 |
48.80 |
|
0.5F |
19/0.19 |
0.3 |
1.6 |
7.07 |
34.60 |
|
0.75F |
19/0.23 |
0.3 |
1.8 |
9.76 |
23.60 |
|
1.25F |
37/0.21 |
0.3 |
2.1 |
14.86 |
14.60 |
|
2F |
37/0.26 |
0.4 |
2.6 |
22.78 |
9.50 |
| Note: The “F” in the table indicates that the conductor is a soft structure | |||||
.
✔ German standard
● Characteristic: German standard wire insulation is thinner and more flexible
● Example: DIN_ 72550,DIN72551,DIN_ 76772,VW_ 60306,LV_ 112-3

✔ American Standard
● Characteristic: The insulation skin of American standard wire is generally thermoplastic or thermosetting elastomer, and it is also processed by irradiation process. American standard wires are characterized by thin insulation and excellent heat resistance.
● Example: SAE_ J1128,SAE_ J1678, USCAR-21
|
AWG |
Diameter |
Turns of wire, |
Area |
Copper wire |
||||||||
|
Resistance per unit length] |
Max I at 4 A/mm2 current density |
Ampacity at temperature rating |
||||||||||
|
60 °C |
75 °C |
90 °C |
||||||||||
|
(in) |
(mm) |
(Per in) |
(Per cm) |
(kcmil) |
(mm2) |
(mΩ/m) |
(mΩ/ft]) |
(A) |
||||
|
10 |
0.1019 |
2.588 |
9.81 |
3.86 |
10.4 |
5.26 |
3.277 |
0.9989 |
21.0 |
30 |
35 |
40 |
|
12 |
0.0808 |
2.053 |
12.4 |
4.87 |
6.53 |
3.31 |
5.211 |
1.588 |
13.2 |
20 |
25 |
30 |
|
14 |
0.0641 |
1.628 |
15.6 |
6.14 |
4.11 |
2.08 |
8.286 |
2.525 |
8.3 |
15 |
20 |
25 |
|
16 |
0.0508 |
1.291 |
19.7 |
7.75 |
2.58 |
1.31 |
13.17 |
4.016 |
5.2 |
— |
— |
18 |
|
18 |
0.0403 |
1.024 |
24.8 |
9.77 |
1.62 |
0.823 |
20.95 |
6.385 |
3.3 |
10 |
14 |
16 |
|
20 |
0.0320 |
0.812 |
31.3 |
12.3 |
1.02 |
0.518 |
33.31 |
10.15 |
2.1 |
5 |
11 |
— |
|
22 |
0.0253 |
0.644 |
39.5 |
15.5 |
0.642 |
0.326 |
52.96 |
16.14 |
1.3 |
3 |
7 |
— |
.
4. Classification of Automotive Wire
Automotive wire can be basically distinguished by Variety, Size, Color and Anti-interference ability.
4.1 Variety
“Variety” are mainly differentiated according to the different insulation layers. Common insulation materials in cables include oil-impregnated paper, PVC, polyethylene, cross-linked polyethylene, rubber, etc.
 4.2 Size
4.2 Size
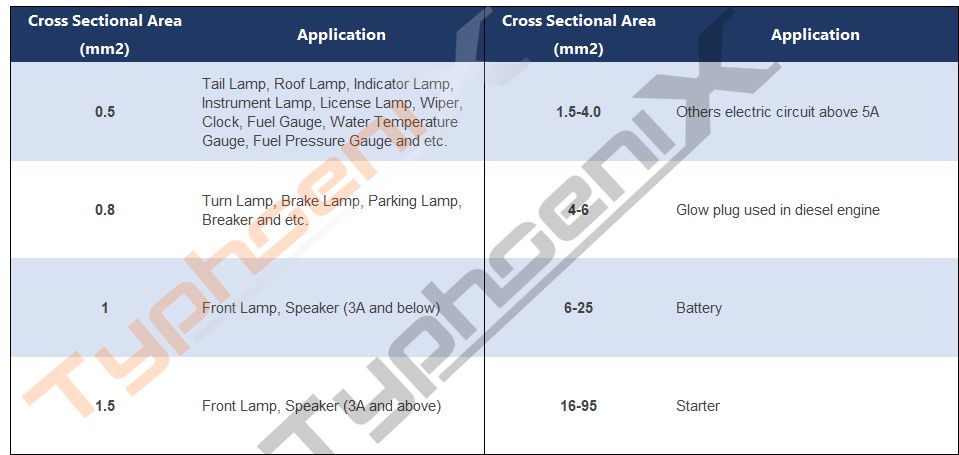
“Size” is distinguished according to the coarse or fine of the core wire, which is mostly expressed by the cross-section area of the core wire. There are different specifications: 0.35, 0.5, 0.8, 1.0, 1.25, 2.0, 4.0, 6.0, 10.0, 15.0, 25.0, etc.
✔ Cross-Section Area of Single Wire (Single Core Cable)
 The cross-section area of a round single wire are calculated as
The cross-section area of a round single wire are calculated as
A = π R2
A : cross-section area (mm2)
R: radius= diameter /2(mm)
 ✔ Cross-Section Area of Bunched Wire (Multi-Core Cable)
✔ Cross-Section Area of Bunched Wire (Multi-Core Cable)
 The cross-section area of bunched wires (stranded wires) are calculated as
The cross-section area of bunched wires (stranded wires) are calculated as
A = n π R2
A : cross-section area (mm2)
n : number of wires
R :single wire radius= single wire diameter /2 (mm)
 The wire specifications will indicate the number of copper wires and the diameter (maximum/minimum) of copper wires in a single wire, so we can quickly estimate the wire “SIZE” according to the above formula, which is very useful for matching German, Japanese and American standard wires. The wire pairing table of three standard specifications is as follows:
The wire specifications will indicate the number of copper wires and the diameter (maximum/minimum) of copper wires in a single wire, so we can quickly estimate the wire “SIZE” according to the above formula, which is very useful for matching German, Japanese and American standard wires. The wire pairing table of three standard specifications is as follows:
<img ” src=”/uploads/三国电线规格对照表-带水印.png” alt=”三国电线规格对照表-带水印” itemprop=”image”>
Recommended nominal sectional area of main line conductor of 12V power system:

4.3 Color
“Color” refers to the color of the insulating layer, which is generally divided into Single-color wire and Double-color wire.
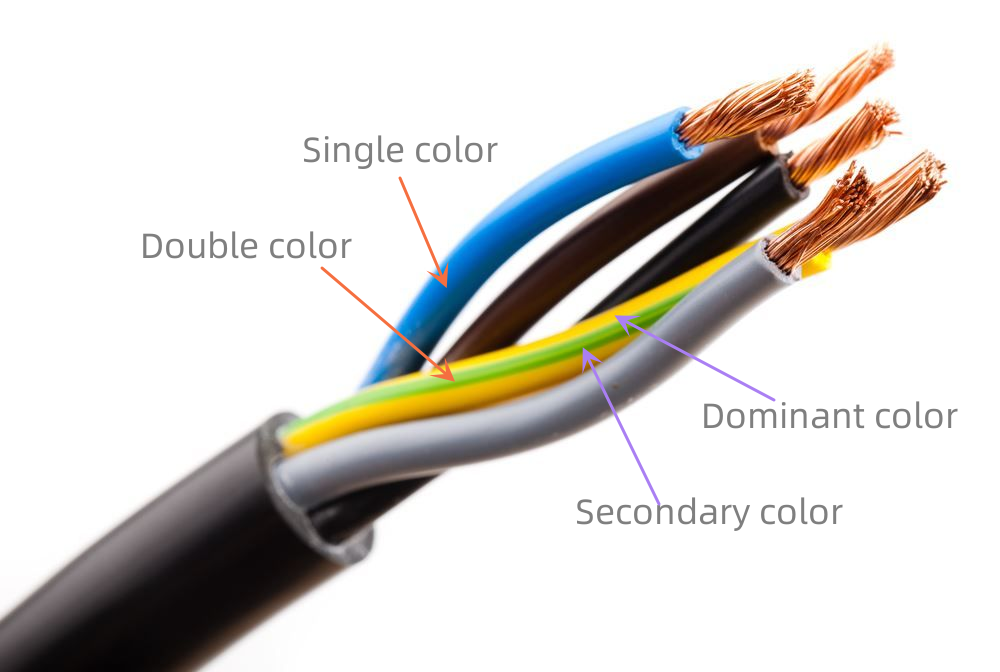
 ✔ Single-color wire: The insulation of wire has one color.
✔ Single-color wire: The insulation of wire has one color.
Generally, the color code of a monochromatic conductor is indicated by its English initials:
✔ Double-color wire: wire with two colors of insulating surface. The color code is expressed in the form of a combination of English initials according to the order of dominant and secondary colors.
 ● Dominant color: also known as background color, with a wide color band and a large proportion of insulation surface area.
● Dominant color: also known as background color, with a wide color band and a large proportion of insulation surface area.
● Secondary color: also known as stripe color or logo color, with a narrow color band and a small proportion of insulation surface area.
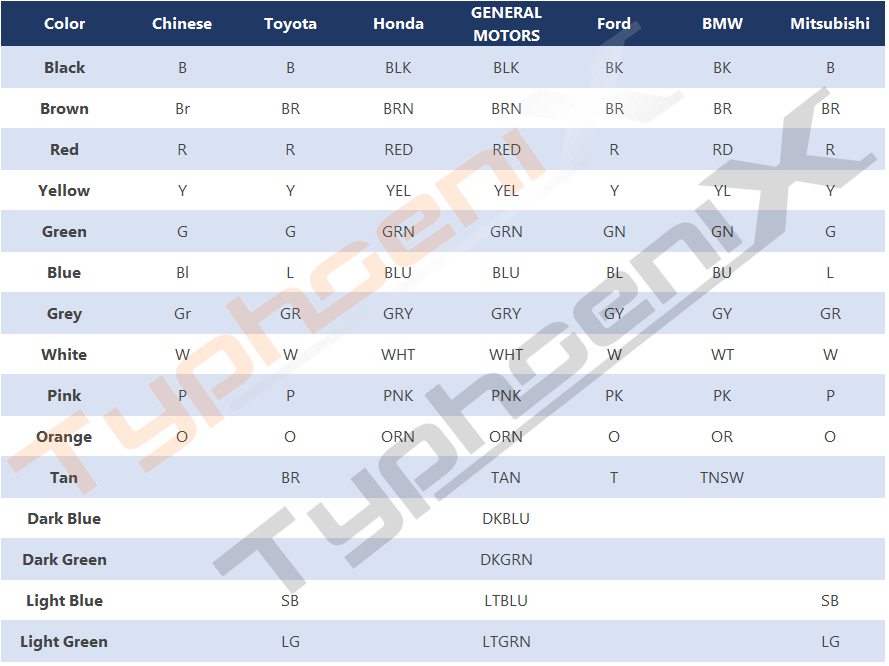
 Most automobile manufacturers in various countries use English letters to indicate the color of wire sheaths and stripes on circuit diagrams. See the following table for wire color codes of common models:
Most automobile manufacturers in various countries use English letters to indicate the color of wire sheaths and stripes on circuit diagrams. See the following table for wire color codes of common models:


★ Selection principle to choose the automotive wire colors:
 ● Single-color is preferred, then Double color.
● Single-color is preferred, then Double color.
● The black wire shall not be used for other purposes, if the grounding wire of the harness use black wire.
● The main power cord is preferably monochrome, which should be red, and two kinds of Double-color wire can be added, the dominant color is red, the secondary color is white or black.
● In the same branch wire of wire harness, wires with the same specification and color are generally not selected to prevent confusion during wire harness processing.
● In principle, the same wire color cannot be used in the one connector housing. If the wire diameter difference is large, the same color wire can be considered.
● In the design of a wire harness, wires with the same wire diameter and color cannot be used, and when selecting the color, try to choose the color combination with obvious contrast and easy to distinguish by eyes.
● The selection of conductor color shall be conducive to reference management, and new conductor varieties shall be avoided as far as possible.
 4.4 Anti-interference Capability
4.4 Anti-interference Capability
Automobile wires can be divided into Ordinary wires, twisted pair wires and Shielded wires according to their purposes.

✔ Twisted pair wire
Twisted pair is the simplest way, that is, the harness formed by winding two mutually insulated wires together according to certain specifications.
The signals generated on them are equal in size and opposite in direction, which can cancel each other, to reduce the interference of their own signals to the outside world and prevent the interference of external electromagnetic.
✔ Shielded wire
The anti-interference ability is better than twisted pair, which is the addition of metal shielding layer between twisted pair and external insulation layer. Common shielding wires are aluminum foil shielding wire and braided screen shielding wire.
Its principle can be simply understood as that the interference signal flows through the shielding layer (aluminum foil, woven mesh) without contacting the communication signal, to achieve the purpose of anti-interference.

Post time: Feb-16-2023

